Rusmidler i Norge 2008
|
|
|
- Benedicte Farstad
- 7 år siden
- Visninger:
Transkript
1 Statistikk Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway Alkoholpolitikk i kommunene Alcohol Policy in the Municipalities Redaktør (Editor): Anders Bryhni Redaksjonsutvalg (Editorial group): Anne Line Bretteville-Jensen, Elin K. Bye, Ragnar Hauge, Sturla Nordlund, Hege C. Lauritzen og Astrid Skretting Utgitt av: Statens institutt for rusmiddelforskning Produced by: Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Design og trykk (print): ISBN Sirus SIRUS Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research
2 Forord Preface Forord Preface 3 Preface This publication, produced by the Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research (SIRUS), once again presents a selection of statistics on alcohol and drugs. The figures have been collected from public statistics and special studies. Alcohol and Drugs in Norway 2008 is the twentieth in a series of yearly publications in which updated figures are presented on the use of alcohol, addictive legal and illegal drugs, and on the availability, economic aspects, damage/injuries and crime associated with such substances. Until 2000 the data were collected and published in collaboration between the Norwegian Directorate for the Prevention of Alcohol and Drug Problems and the National Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research (SIFA). As a consequence of the reorganisation of the national responsibilities in the alcohol and drug field, SIFA and the statistical section of the Directorate were amalgated as of 1 January This resulted in a new institute, SIRUS, which now has the sole responsibility for the publication. Every other year s edition includes the more detailed presentation of a special theme, this year the subject being Alcohol Policy - A Municipal Responsibility. In 1990 the theme was Alcohol Consumption since the Second World War, in 1992 Drugs and Drug Use, in 1994 Alcohol in the Nordic Countries, in 1996 Alcohol: Sales, Licences and Economy, in 1998 Drugs and Drug Use once again, in 2000 Alcohol and Drugs in the Nordic Countries, in 2002 Norwegian and Nordic Alcohol Policy and the EU, in 2004 Drugs and Treatment, and in 2006 Norwegian Drinking Patterns. All the figures presented here are to be found in the databases at SIRUS. For some areas long data time series are available in much greater detail which are, however, too extensive for inclusion in the present booklet. Some of these have been published before and can be found in earlier editions of Alcohol and Drugs in Norway, particularly in the 1991 edition. In some areas, the databases contain more detailed statistics than those which are presented here. All tables are available in our online database at no. This publication is intended to be a resource for everyone who wishes to have statistical documentation of the alcohol and drug situation in Norway. We hope that it will be useful for people who work with the dissemination of information and the planning and implementation of preventive programmes, for researchers, and for everyone with a general interest in this field. In order to make this book more available to people outside Norway, the complete text has been translated into English. Oslo, December 2008 Jostein Rise Director
3 8 Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway 2008 Contents Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility by Hege C. Lauritzen Appendix Tables Sales of alcohol Table Annual sales of alcohol in some European countries measured in litres of pure alcohol per inhabitant Figure 1.1a Annual sales of alcohol in five European countries Figure 1.1b Annual sales of alcohol in five European countries Table Annual sales of spirits in some European countries measured in litres of pure alcohol per inhabitant Figure 1.2a Sales of spirits in some European countries Figure 1.2b Annual sales of spirits in five European countries Table Annual sales of wine in some European countries measured in litres per inhabitant Figure 1.3a Sales of wine in some European countries Figure 1.3b Annual sales of wine in five European countries Table Annual sales of beer in some European countries measured in litres per inhabitant Figure 1.4a Sales of beer in some European countries Figure 1.4b Annual sales of beer in five European countries Table Annual sales of alcohol in the Nordic countries measured in litres of pure alcohol per inhabitant aged 15 years and over Figure Annual sales of alcohol in the Nordic countries Table Annual sales of alcohol in Norway in total in 1000 litres and in 1000 litres of pure alcohol Table Annual sales of alcohol in Norway per inhabitant aged 15 years and over in litres and in litres of pure alcohol Figure 1.7a Annual sales of alcohol in Norway Figure 1.7b Percentage of sales for the different types of alcohol in Norway and 2007
4 Innhold Contents 9 Table Annual sales of different types of beer in Norway in 1000 litres and in 1000 litres pure alcohol Table Annual sales of different types of beer in Norway Measured in litres of pure alcohol per inhabitant aged 15 years and over Economy and alcohol Table Real price indices for spirits, fortified wines, table wines and beer Table Index for the relationship between nominal price index for different types of alcoholic beverages and index for nominal wages and salaries from the National Account Table Consumers expenditure on spirits, wine and beer. Total expenditure in millions of Norwegian kroner and expenditure on alcohol as a percentage of household consumption Table Consumers expenditure on spirits, wine and beer per inhabitant aged 18 years and over in Norwegian kroner Table Excise duty on wine and spirits. Basic duty in Norwegian øre (100 øre = 1 krone) per percent alcohol by volume per litre Figure Basic duty on spirits and wine Table Excise duty on beer in Norwegian kroner per litre and classification of beer before and after Table Government revenue from the sale of alcohol in millions of Norwegian kroner Alcohol-related mortality and crime Table Number of deaths caused by alcohol by diagnosis and gender (underlying cause of death) Table Number of deaths caused by alcohol by age and gender (underlying cause of death) Table Number of deaths caused by alcohol by age and gender (total number of deaths over a period of 19 years, ) Table Number of deaths caused by cirrhosis of the liver in total and per inhabitants by gender Figure Number of deaths caused by cirrhosis of the liver by gender Table Number of admissions to somatic hospitals with alcohol related underlying diagnosis Figure Number of admissions to somatic hospitals with alcohol related underlying diagnoses Table Number of sanctions in cases involving misdemeanours against Act no. 27 on the sale of alcoholic beverages or against the Customs Act by type of misdemeanour Table Number of sanctions for illicit distilling by county
5 10 Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway 2008 Driving under the influence Table Number of tests from drivers by type of suspicion (alcohol and/or drugs) Figure Number of tests from drivers by type of suspicion alcohol and other drugs Table Number of tests from drivers by type of suspicion and gender (alcohol and/or drugs) Table Number of tests from drivers, which are tested positive for drugs Table Number of sanctions for driving under the influence of alcohol and/or drugs as a percentage of all sanctions for traffic misdemeanours Table Number of sanctions for driving under the influence of alcohol and/or drugs by county Table Number of sanctions for driving under the influence of alcohol and/or drugs per 10,000 inhabitants aged 18 years and over by county Figure Number of sanctions for driving under the influence of alcohol and/or drugs per 10,000 inhabitants aged 18 years and over by county Drug statistics Table Table Deaths caused by use of drugs by gender and age according to Statistics Norway (underlying cause of death) Table Deaths caused by use of drugs by gender and age according to KRIPOS Table Number of seizures of opiates, cannabis, amphetamines and cocaine Figure Number of seizures of cannabis, heroin, cocaine, and amphetamine Table Number of seizures of ecstasy, LSD, khat, magic mushrooms, GHB and tranquillisers Figure Number of seizures of ecstasy, LSD and khat Table Amount of confiscated opiates, cocaine, cannabis and amphetamines in kilogrammes Table Amount of confiscated ecstasy, LSD, khat, magic mushrooms and tranquillisers Table Number of drug offences reported Figure Number of drug offences reported Deaths caused by use of drugs by gender according to the National Bureau of Crime investigation (KRIPOS) and Statistics Norway (underlying cause of death)
6 Innhold Contents 11 Studies on the use of alcohol and drugs by young people Table Percentage of young people in Norway who have at some time drunk alcohol by gender and age Table Percentage of young people in Oslo aged years who have at some time drunk alcohol by gender and age Table Percentage of young people in Norway aged years who mean that cannabis should be sold freely and who would try it if there were no danger of being arrested Table Percentage of young people in Oslo aged years who mean that cannabis should be sold freely and who would try it if there were no danger of being arrested Table Estimated annual consumption measured in litres of pure alcohol by type of beverage among young people in Norway aged years Table Estimated annual consumption measured in litres of pure alcohol for young people in Norway aged years, by age and gender Table Mean age of drinking as much as one bottle of beer, one decilitre of wine or 0.2 decilitre of spirits in Oslo and Norway Table Percentage of young people in Norway aged years who say that they have at some time used different drugs Table Percentage of young people in Oslo aged years who say that they have at some time used different drugs Figure 6.7a Percentage of young people in Oslo who say that they have at some time used different drugs Figure 6.7b Percentage of young people in Oslo and Norway who say that they have at some time used different drugs. 2008
7
8 Hege C. Lauritzen Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility Alkoholpolitikk - et kommunalt ansvar
9 30 Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility The sale of alcohol in Norway is subject to statutory regulations, i.e. Act on the Sale of Alcoholic Beverages (Alcohol Act) of June 2, The act states that the reason for regulating the import and sale of alcoholic beverages is to reduce the social and personal cost of alcohol consumption. There is wide scientific consensus that regulatory measures such as the Alcohol Act offer one of the most effective means of reducing alcohol-related harm (Babor et al. 2003). To sell alcohol in Norway, a vendor requires a license. Apart from airlines, the Norwegian State Railway (NSB), passenger ships and commissioned and non-commissioned officers messes, which are licensed by the state, the municipal council is the licensing authority. The system is known as the municipal licensing system, and it originated in the 1830s. Over the years, municipalities have enjoyed ever wider powers to shape alcohol policy. The principle of municipal autonomy is the bedrock on which Norwegian alcohol policy rests (Hauge 1986). The state monopoly system for the sale of wine, spirits and strong beer, and the municipal licensing system are the two most important mechanisms of controlling the sale of alcohol in Norway. To ascertain how alcohol policy in Norway is implemented in practice, reliable information is crucial. In 1989, the then Norwegian Directorate for the Prevention of Alcohol and Drug Problems (Rusmiddeldirektoratet) was commissioned to study the practical implementation of the Alcohol Act in every municipality in the country (Municipal Survey). This task passed to the National Institute for Drug and Alcohol Research (SIRUS) when it came into being in Up to and including 1994, Statistics Norway collected data relating to licensed establishments (i.e., licensed to retail or serve alcoholic beverages). In 1995, however, this task too was incorporated under the Municipal Survey. In Norway, we have statistics on both types of license that go back to Information is obtained by sending a questionnaire to every local authority in the country at the start of every year. Local authorities submit a situation report at the close of the preceding year. Many of the questions have remained the same since 1989, allowing for comparisons across time. New questions have been introduced, particularly after the revision of the Alcohol Act in Response rates are very high indeed between 95 and 99 per cent. Every year, a few municipalities fail to respond, but they tend to be small and seldom fail two years running. Fifteen municipalities failed to respond in As they had responded in 2007, however, we have extrapolated data from 2007 for use in the 2008 survey. In light of response failures over the years, the data as presented may suffer from some minor reporting errors. This article describes and discusses data and prevailing tendencies. A detailed report including comparisons between geographical areas and years can be found on our website, 2 Retail licenses fewer stores stocking medium strength beer On July , several amendments to the Alcohol Act and relevant regulations came into force. One of them introduced a new way of classifying alcoholic beverages, cf. the Alcohol Regulation (Alkoholforskriften) 1.1. Alcoholic beverages used to be differentiated on the basis of production method, i.e., beer, wine and spirits. The new system relies on alcohol content. Beverages containing the same amount of alcohol by volume (ABV) are grouped in the same category. (The definition of spirits/liquor was retained, nevertheless, because several provisions in the Act refer to spirits alone.) The old and new classification schemes are shown below. Current legislation refers of course to the new one.
10 Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility 31 Table 1 Categories of alcoholic beverages New classification Old classification Alcoholic beverages category 1 All beverages over 2.5 and Beer under 4.7 per cent alcohol by volume Alcoholic beverages category 2 Strong beer and wine. All beverages over 4.7 and spirits under 22 per cent below 22 per cent alcohol alcohol by volume by volume Alcoholic beverages category 3 All beverages between 22 Spirits and 60 per cent alcohol by volume Statistics on the number of retail outlets go back to As the graph below shows (figure 1), the number of business enterprises licensed to sell medium strength beer grew steadily from 1930, peaking in 1970 with nearly 7,000 outlets. Figure 1 Graph depicting number of retailers licensed to sell medium strength beer and similar beverages, Section 1 4 of the Alcohol Act defines the retailing of alcohol as «the supplying of alcoholic beverages to the consumer in return for payment for consumption off the premises». Under section 3 1 of the Alcohol Act, alcoholic beverages «may only be retailed on the basis of a municipal licence». For the retail of wine, spirits and strong beer, only local outlets under state owned AS Vinmonopolet can be given licenses. Apart from approving and rejecting retail license applications, municipalities are authorized to decide where medium strength beer and similar beverages1 may or may not be retailed. Should, for instance, it be sold by the local grocery store or supermarket, or only from a beer monopoly? The municipality cannot grant retail licenses to filling stations or kiosks (section 3 4, Alcohol Regulations). If the Vinmonopol has an outlet in the municipality, under section 3 1 of the Alcohol Act, one or more licenses must be issued for the retailing of medium strength beer and similar beverages By 1980, the number had fallen to 4,637 an extremely sharp 32 per cent decline in the space of only a decade. The main cause was structural. The retail business was rationalising and consolidating and many grocery stores fell by the wayside. The level of accessibility fell, but not necessarily because of policy decisions on the part of the individual municipality. As of 2007, medium strength beer and similar beverages are sold in every municipality in the country, and retailed in most of them by supermarkets. As already mentioned, municipalities can decide to have medium strength beer retailed by a beer monopoly (cf. section 3 1 of the Alcohol Act). The municipality may also issue a license to a business enterprise to retail only medium strength beer and similar beverages, along with non-alcoholic beverages, or it may decide to operate its own municipal beer monopoly. Table 2 shows changes in the number of retailers licensed to sell the different categories between 1930 and For the purposes of this report, alcoholic beverage group 1 (more than 2.5 and less than 4.7 per cent ABV) will be referred to as medium strength beer and similar beverages. This is because the class also contains «alcopops» and cider with the same amount of alcohol. The beer monopoly scheme originated in In that year, the Parliament (Stortinget) passed a law allowing retailers to sell beer and wine in towns and cities. This purpose was to exclude
11 32 Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway 2008 private commercial interests from the sale of alcohol. In municipalities with a «beer monopoly», breweries were allowed to sell their own produce (Hauge 1986). A 1989 amendment to the law gave municipalities the authority to establish and manage retail businesses for beer (municipal beer monopolies). In 1990, the municipality of Stranda, in the county of Møre og Romsdal, became the first municipality to establish such a beer monopoly. Within a year, the number of municipalities had grown to six; and five years later, in 1995, there were nine. By 1998, eleven municipalities had fourteen municipal beer monopolies between them (Grytten 1997). Since then, the beer monopoly scheme has declined. By 2007, according to reports, only four municipalities (Hareid, Lyngdal, Sogndal and Ulstein) retained the scheme. The private beer monopoly is an older variant, and also more widespread than the municipal beer monopoly. There were twenty five private beer monopolies in 1997, in as many municipalities. Like the municipal beer monopoly, decline has characterised the private ones. In 2007, five municipalities (Fauske, Førde, Kautokeino, Vefsn og Vågan) had ten private beer monopoly outlets among them. There were forty private beer retailers in These establishments tend to be run by breweries. Breweries did not require a municipal licence until 1996, when the Alcohol Act was brought into harmony with the European Economic Area (EEA) agreement. New legislation removed the right of breweries to sell their own produce over the counter without a retail license. Breweries can still sell their produce, but now need a municipal retail license to do so. In addition, sixty eight municipalities reported that they occasionally organised sale of category 1 alcoholic beverages differently than via ordinary retailers or their own beer retail enterprise. This was often outlets connected with camping sites and cabin rentals. Alcoholic fruit beverages (i.e., «alcopops») were retailed by the Vinmonopol until After a ruling of the EFTA Court, Norway was required to treat alcoholic beverages in the same category in the same way. So from January 1, 2003, licensed retailers could begin to sell alcopops. There was an sudden rise in the number of retailers, from 188 to 4,299, and the volume of alcopops sold over the counter rose from 0.07 litres pure alcohol per head of population aged 15 and over in 2002 to 0.22 litres in 2003 (Rusmidler i Norge 2007). In a bid to halt the rise in consumption, Parliament decided to levy a liquor tax on alcopops. This came into effect on January 1, 2004, and led to higher prices in the shops. Again the effect was immediate: sales fell back to 0.11 litres pure alcohol in the course of the year. Only the Vinmonopol has the right to retail spirits, wine and alcoholic beverages with more than 4.7 per cent alcohol by volume (ABV), but it needs a municipal retail license to do so. Vinmonopol outlets are only allowed in municipalities which permit the retailing of beer below 4.76 per cent ABV. When Vinmonopolet opens a new outlet, the municipality therefore already has at least one business enterprise licensed to retail medium strength beer and similar beverages. The siting of alcohol outlets and the manner in which the beverages are sold by the Vinmonopol (over the counter or self-service) must also be approved by the municipal council. In 2007, there were 222 Vinmonopol outlets in Norway. Figure 2 Growth in numbers of Vinmonopol retail outlets As Figure 2 shows, the number of Vinmonopol outlets grew steadily from 1930 to From 1995 to 2000, twenty eight new outlets opened,
12 Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility 33 and from 2000 to 2005, a further fifty eight. By the end of 2007, there were 222 Vinmonopol retail outlets altogether, spread across 172 municipalities in every county of the country. According to signals coming from AS Vinmonopolet, there are plans to open 22 new outlets in By the end of 2008, we will therefore have 244 outlets (AS Vinmonopolet, Annual Report 2007). The first self-service Vinmonopol outlets opened in 1999 on a pilot basis. During the evaluation period of two years, sales volume increased on average by 10 per cent (Horverak 2002). The Ministry of Health and Social Affairs decided nevertheless to convert the trial into a permanent arrangement because, as they put it, there was a need for modern, effective and customer-friendly Vinmonopol outlets (Rundskriv I ). Municipalities still have the power to require that spirits, wine and strong beer are retailed over the counter as a licensing condition of all or some retailers within the municipality s own jurisdiction. Very few municipalities avail themselves of this. In 2007, 97 per cent were self-service outlets. 3 Three-fold rise in the number of licensed premises As in the case of retail licenses, the municipal council is the licensing authority for establishments which serve alcoholic beverages for consumption on the premises (section 1 4, Alcohol Act). Licensees may not allow customers to remove alcoholic beverages purchased on the premises from the delineated area for serving. paragraph), State licenses (sections 5 2 and 5 3, Alcohol Act) and ambulatory licenses (section 4 5, Alcohol Act), or licenses issued for a certain period of the year or a specific event (section 1 6, Alcohol Act, third paragraph). Figure 3 Graph depicting growth in the number of licensed premises, Between 1955 and 1980, the number of licensed premises rose at a relatively measured pace, from 1,409 to 2,439. Over a period of twenty-five years, in other words, the number of licensed premises doubled. But between 1980 and 2007 growth accelerated sharply, from 2,439 to 7,332 tripling in under thirty years. Another interesting development is the change in the combination of licenses. The authorities can determine which alcohol groups to include in a particular license. A license may, for instance, include all types of alcoholic beverage, or only wine and beer (i.e., categories 1 & 2). When a license to serve spirits (i.e., category 3) is issued, the licence must necessarily include beer and wine. Figure 4 Number of on-licenses by license combination for the years 1955, 1980 and The municipalities are virtually autonomous in questions to do with on-licenses. As section 1 7 of the Alcohol Act states, «licences to retail and serve alcoholic beverages is granted by the municipality unless a State licence is granted». The number of licensed establishments has been growing since the 1950s. The graph reproduced below does not include temporary licenses for private functions (section 4 2, Alcohol Act, second 100 % 90 % 80 % 70 % 60 % 50 % 40 % 30 % 20 % 10 % 0 % Group 1 Group 2 Group 3
13 34 Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway 2008 Figure 4 shows variations in the composition of municipal serving licenses issued at different points in time. In 1955, only 6 per cent of 1,409 serving licenses authorized the holder to serve spirits. Nearly half covered only medium strength beer. At that time, licenses to serve spirits were issued by AS Vinmonopol, which could «sub-lease» the number of rights that had been granted for serving spirits at hotels and restaurants. Spirits could only be served in municipalities with a population head above 4,000. A license to serve spirits could only be obtained in municipalities where the Vinmonopol had one of its outlets. A plebiscite of municipal residents was required to determine whether liquor should be sold or not. If at least 5 per cent of a municipality s population petitioned the authorities, they were required by law to hold such a plebiscite. In 1985, 863 or 28 per cent of a total of 3,119 serving licenses authorized the holder to serve spirits, wine and beer a rise from 6 per cent over a thirty year period. The number of medium strength beer-only licenses decreased to 14 per cent. Several developments had an effect on municipal serving licensing in this period. In 1967, the law was amended to allow the sale of spirits in all municipalities, irrespective of population size. The State Licensing Board for the Sale of Spirits was appointed that year, and the provision requiring municipalities to hold a binding plebiscite on the sale of spirits was removed. Until 1971, spirits could not be served unless the municipality had at least one Vinmonopol outlet. Serving licenses include spirits to an increasing extent. In 1995, not quite half of all licensed premises could serve spirits. The number of medium strength beer-only licenses had fallen to 3 per cent. The new Alcohol Act of 1989 delegated more authority to the municipalities. The provision under which binding plebiscites had to be held if at least 5 per cent of the electorate lodged a petition, was repealed. The State Licensing Board was phased out and the municipal council vested with the authority to decide whether spirits could be served. Vinmonopol s status as the license holder for the serving of spirits in a municipality along with the opportunity to restrict the sale of spirits to «travellers» and «in connection with a meal» were also terminated. A new rule was introduced under which holders of licenses to serve liquor had to have some tangible connection with the actual place of business, as in case of licenses to serve beer and wine (Hauge 2000). By 2007, nearly all serving licenses included spirits as well (82 per cent). Licenses for medium strength beer (alcohol beverage category 1) are granted only in exceptional cases. In 2007, the number of these licenses accounted for less than 1 per cent. Licensed premises or a license to serve alcoholic beverages tend terminologically to imply bars which serve beer, wine and spirits or restaurants which serve alcoholic beverages in connection with a meal. In recent years, however, licenses are also being issued for less conventional undertakings. The local council may decide to let retirement and nursing homes dispense alcohol, and seventy local councils did precisely this in Six municipalities report issuing serving licenses to hairdressers, seven to spas, and five to specialist retailers including a furniture emporium for example. 4 Licensing practices The Alcohol Act gives local councils considerable flexibility in the design and implementation of alcohol policies. A municipality might decide to ban the sale and serving of alcohol altogether. In 2007, alcohol was sold in every municipality in the land, but two held back on granting serving licenses (Audnedal and Siljan).
14 Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility 35 Figure 5 Municipalities without retail or serving establishments with a municipal alcohol license In per cent Without retail licenses Without serving licenses Without either Limiting the number of licenses With the 1997 revision of the Alcohol Act, a new provision came into being allowing local authorities to set a ceiling on the number of retail and serving licenses (section 1 7a, Alcohol Act, third paragraph). Although the provision was new, legal practice had already given local authorities the power to impose ceilings (Hauge and Lohiniva 2002). Figure 6 Municipalities with ceilings in place to limit the number of licenses to retail or serve alcoholic beverages In per cent If we turn the clock back about thirty years, the situation was very different indeed. Data from 1980 show that alcohol was unavailable in 20 per cent of municipalities both to drink on the premises and take home. By 1990, the percentage had fallen to 12. Municipalities without serving licenses had declined to 8 per cent, and only 3 per cent had neither serving nor retail licensees. Only two local authorities in 1990 reported no retail outlets for alcoholic beverages, while eight were still without a licensed hospitality business was the first year without a completely «dry» municipality. The last such municipality was Audnedal in the county of Vest Agder. Municipalities have several other mechanisms at their disposal to try to influence alcohol use apart from granting or withdrawing licenses. In 1997, the Alcohol Act was thoroughly revised with a view to curbing white-collar crime in the hospitality trade. One of the reasons for revising the act, the proposal stated, was to increase awareness of local authorities of their opportunities to tighten alcohol policy (Ot prp nr 7). A provision was included in the revised act whereby the authorities could impose additional conditions and make it easier to withdraw a license and impose a limit to the number of hours alcohol could be retailed and served Retail Serving As Figure 6 shows, municipalities set ceilings on either or both types of license in decreasing numbers. In 1995, 75 (17 per cent) had a ceiling on retail licenses. By 2007, the number had fallen to 23 (5 per cent). Ceilings on serving licenses show a similar decline. In 1995, 80 local authorities (18 per cent) operated with a ceiling on licenses to serve alcohol, falling to 34 (18 per cent) in Longer opening hours for retailers and serving hours in the hospitality trade When the Alcohol Act was revised in 1997 the concepts of «normal opening/serving hours» and «maximum opening/serving hours» were introduced. If a municipal council does not itself determine opening and serving hours, the «normal hours» set out in the act shall apply. For the retail of alcoholic beverages, normal opening hours are 08:00 18:00 Monday Friday, and 08:00 15:00 hrs on Saturdays and days preceding public holidays (section 3 7, Alcohol Act).
15 36 Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway 2008 The local council may, however, restrict or extend opening hours for every retailer or selected retailers in the municipality. Retailing and delivery are nonetheless prohibited after 20:00 hrs on weekdays, and 18:00 hrs on Saturdays and days preceding public holidays (except the day preceding Ascension Day). The council may also decide to ban retailing at particular times of the day or on particular weekdays. It is not usual today, nor was it in the past, to limit the hours to retail alcohol category 1, either for all or some retailers. Municipality-wide restrictions fell sharply from 1998 (11 per cent) to 2005 (3 per cent). On the contrary, the tendency is to extend retailing hours. In 1998, 168 municipal councils extended hours to retail alcohol category 1 beverages for all retailers. By 2007, 256 municipalities had taken a similar step, i.e., 59 per cent of the country s local councils operated with extended retail hours. The normal hours for the serving of alcoholic beverages with an ABV percentage of 22 or more are 13:00 24:00. Beverages with a lower ABV percentage can generally be served between 08:00 and 01:00. The local council may extend serving hours, but licensees are not allowed to serve alcoholic beverages containing 22 per cent ABV or more between 03:00 and 13:00. Alcoholic beverages in the lower range cannot be served between 03:00 and 06:00. Finally, category 3 drinks cannot be served unless the other categories are also available. A very small number of municipalities enforce shorter serving hours than the law permits for beverages in categories 1 and 2. While reducing serving hours is extremely rare, councils are much more likely to grant extensions. In 2007, 250 municipalities (58 per cent) extended serving hours for spirits for all vendors in the municipality, which is slightly less than the previous year. There were 101 municipalities that had granted extended serving hours to individual licensed premises, representing a year-on-year increase. 4.3 More and tighter criteria Sections 3 2 and 4 3 of the Alcohol Act authoritize local councils to attach conditions to a license whether it be to retail or serve alcohol. The Alcohol Act was revised in 1997 with a view to delegating greater powers to local government to shape the alcohol policy of their liking. Previously, councils could only require licensees to observe certain opening and serving hours; to ban the sale of alcohol in the vicinity of an auction; or to limit the scope of a serving license to travellers and customers partaking of a meal (Hauge and Lohiniva 2002). Whatever the conditions, however, they could not violate provisions set out in administrative law, and had to be justified by reasons of alcohol policy. General conditions can be attached to every license, or specific conditions to specific licenses. Very few local councils attach conditions to retail licenses. The number of municipalities where such criteria are in force rose from thirteen in 1998 to twenty eight in Of these twenty eight, eighteen specified the conditions they had enforced. One municipality required retailers to sell beverages over the counter, another introduced weekly retail-free days. In addition, sixteen municipalities banned retailers from placing alcoholic beverages near entrances/exits and checkouts. In 2007, 128 municipalities said they had attached conditions to licenses. With regard to the nature of the conditions, 48 municipalities required the premises to hire a security guard 39 municipalities banned the serving of spirits out of doors 137 municipalities required approval of premises by municipal planning and building authorities 30 municipalities specified a higher age limit 16 municipalities required staff to attend courses on responsible serving
16 Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility municipalities required customers to buy food 8 municipalities required a specific ratio between alcohol and food sales We see a tendency for municipalities to attach conditions to serving licenses, though the reasons for doing so are not necessarily connected with alcohol policy. 4.4 Rejected applications Local authorities may reject applications for both types of license under the provisions of the Alcohol Act which require the applicant to demonstrate a spotless reputation. The authorities are also permitted under the Act to exercise discretion. Not many municipalities reject applications to serve alcoholic beverages. In 2001, 17 per cent of municipalities had denied such an application. By 2007 the figure had falled to 12 per cent. Several reasons are given: 20 municipalities referred to the past economic conduct of the applicant 16 municipalities referred to the applicant s conduct in relation to alcohol legislation 15 municipalities referred to political concerns locally, such as vicinity to school, danger of too many licensed establishments in a restricted area etc. 14 municipalities referred to other reasons Even fewer local authorities rejected applications to retail alcoholic beverages. In 2001, the proportion was 5 per cent, which by 2007 had diminished to 2 per cent. It is important to note here that rejections do not apply to license renewals, insofar as renewals are dealt with at the start of a new licensing period. A licensing period normally lasts four years marks the start of a new four-year licensing period. There is another explanation for the small number of rejections. Potential licensees will usually have obtained information setting out the criteria on which a license can be granted, including a spotless reputation for economic conduct, for instance. People who do not satisfy the conditions will therefore not apply. 5 Control and penalties associated with utilisation of the license The municipal authorities are mandated to ensure that licensees comply with the provisions of the Alcohol Act, its appurtenant regulations and any conditions placed on a particular license (section 1 9, Alcohol Act). Beverages containing more than 4.7 per cent ABV may only be sold by the Vinmonopol, which undertaking also controls its own outlets. Oversight of retail and serving licences is regulated by chapter 9 of the Regulations on the Sale of Alcoholic Beverages (Alcohol Regulations). Should the licensee be shown to have acted irregularly so as to damage his reputation, or violated the provisions of the Alcohol Act or other rules and regulations of relevance to the purpose thereof (section 1 8, Alcohol Act), the authorities may withdraw the license for the remainder of the licensing period or for a shorter period Responsibility for controlling compliance It was with the 1989 introduction of the new Alcohol Act that the municipalities were given a key role to oversee the utilisation of municipal licenses. Up to that point, the Vinmonopol had inspected establishments dispensing spirits, while retailers and other licensed premises were inspected by the local authorities. In practice, however, only a few municipalities had any form of municipal inspection in place, most leaving it to the police to maintain law and order (Hauge and Lohiniva 2002).
17 38 Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway 2008 With the amended act of 1997, licensees were required to document an unblemished economic record. Up to 2005, the municipalities were required to appoint inspection boards. Inspection boards could have a specific mandate to oversee the utilisation of the Alcohol Act or local authorities could instruct an existing committee to do so. In 2005, the regulations requiring municipalities to designate inspection boards was repealed. Duties such as answering inquiries and providing advice to licensees, and designating a manager and a deputy were retained under section 9 2 of the Alcohol Regulations, but with «municipality» substituting for «inspection board» (Sosial- og helsedirektoratets rundskriv IS-12/2005). In 2007, reports showed that 97 municipalities (22 per cent) had delegated oversight duties to the committee on health and social affairs 64 municipalities (15 per cent) had appointed an inspection board 38 municipalities (8 per cent) shared an inter-municipal inspection board 93 municipalities (22 per cent) had delegated oversight duties to the municipal executive board and/or administrative committee 139 municipalities (32 per cent) had delegated oversight duties to another body Almost a third of the municipalities made up the final category, i.e., delegating control responsibilities to «other bodies». Such bodies included, for instance, the fire brigade, security firms, various committees and panels, etc. Section 9 7 of the Alcohol Act reads: Retail and serving establishments shall be inspected as often as required. Each premises shall be inspected at least once a year. Each year the municipality shall perform at least three times as many inspections as the number of retail and serving establishments. Reports submitted by the municipalities give the number of retail licenses as 4,232 and serving licenses 7,332, i.e., 11,564 licenses in all. Assuming the law is observed, there should have been at least 34,692 separate inspections in Unfortunately we lack information on the actual number of inspections, how they proceeded, and what was done. Apart from the number of withdrawn licences, we have little information on the penalties in cases of non-compliance. It is up to each municipality to decide how to organize inspections. Inspections can be performed by council employees or the council may hire external inspectors from private security firms or suchlike. Figure 7 Inspections undertaken in 1995, 2000, 2005 and In per cent Security firms Municipal inspectors Shared inspection arrangements Food Safety Authority There is a growing tendency to farm out inspection duties to security companies. In 2007, 66 per cent of all municipalities engaged such services of a security company. Another 14 per cent had elected to use their own inspectors; these included major cities like Oslo, Bergen, Kristiansand and Tromsø. Some municipalities have other arrangements than those shown in the figure, using fire brigade, students etc. A minority do not perform inspections at all and do not, in consequence, have any inspectors. We have reason to believe that a council s economy plays a role in these matters.
18 Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility 39 But irrespective of how local authorities choose to fulfil their statutory duties, they are also mandated to train inspectors and ensure that inspections are carried out adequately and satisfactorily (cf. section 9 3, Alcohol Regulations). Figure 8 Where responsibility for training inspectors is placed, In per cent Municipal agency 55 Security firm 5 Collaboration with other municipalities 10 No training 2 Fire Brigade 8 Other As the figure shows, a little over half reported hiring a security firm or other private enterprise to train inspectors in In only 20 per cent of cases was training carried out by a municipal agency, and 10 per cent had no training procedures in place at all. Inspections are supposed to oversee compliance with every provision of the Alcohol Act, of related regulations and conditions attached to particular licenses. The Alcohol Regulations make a point of stressing the importance targeting hours of sale and serving, minimum age limits, and ensuring that alcoholic beverages are not retailed or served to persons who are obviously under the influence of alcohol (section 9 4, Alcohol Regulations). Persons under the influence of other legal or illegal substances (drugs) are also comprehended by the ban. A 2004 amendment to the Alcohol Act introduced a provision requiring the authorities to withdraw a licence if drug peddling and or discrimination repeatedly occurred on the premises (cf. straffeloven [The General Civil Penal Code] 349a). 5.2 Cases of contravention and licence withdrawal The licensing authorities may withdraw a license to retail or serve alcoholic beverages (pursuant to section 1 8, Alcohol Act) if the licensee fails to meet his obligations under the Alcohol Act or other provisions laid out in legislation of relevance to the purpose of the Alcohol Act. Similarly, a license may be withdrawn in cases in which the repute of the licensee can no longer be said to be spotless (cf. sections 3 9 and 4 7). In the case of violations, the municipality decides whether to withdraw the license, and for what period. Municipalities tend relatively often to serve the offending licensee with a warning before taking steps to withdraw his license. Although withdrawal is justified in law, the municipality is under no statutory compulsion to do so. A license may be withdrawn for a longer or shorter period depending on the nature and severity of the offence, i.e., from one day to the end of the current licensing period. Anyone who wilfully or through negligence contravenes the Alcohol Act, or is an accomplice to the contravention of, provisions laid down in or in pursuance of this Act, shall be punished by fines or by imprisonment not exceeding six years (cf. section 10, Alcohol Act). Insofar as observed infringements do not necessarily lead to the withdrawal of a license, we include here information on the number of observed cases. The following table shows the incidence of observed violations and of licence withdrawals. Table 3 Observed violations and withdrawals of retail and serving licenses in 2007 Observed violations Withdrawals Number Number of Number Number of of municipalitiepalitiedents munici- of inci- incidents Retail Serving Source: National Institute for Drug and Alcohol Research
19 40 Rusmidler i Norge 2008 Alcohol and Drugs in Norway 2008 In 2007, 54 municipalities observed 82 violations in connection with retail licenses, and 145 municipalities found 627 violations in connection with serving licenses. The figures show that only in a fraction of the cases is the license revoked. Regarding retail licenses, 37 per cent of the observed violations resulted in withdrawal. Only a quarter of violations observed in connection with the serving of alcoholic beverages resulted in withdrawal. Violations of the retail licensing laws can be broken down as follows: 37 per cent for selling to someone under the legal minimum age; 15 per cent for infringing opening hours; 10 per cent for selling to an obviously inebriated customer; 1 per cent for breaches of the good economic repute criterion. As many as 34 per cent reported «other reasons» without specifying what was meant. Examples are minors in charge of the checkout; placement of alcoholic beverages in the wrong place; deficient internal controls; and failure to ask young customers to produce proof of age. Most violations in connection with serving 43 per cent in fact come under the «other reasons» umbrella. Examples include serving outside the specified serving area; deficient internal controls; non-payment of charges; and offences under the advertising rules. Other offences include serving an obviously inebriated customer (38 per cent of reported incidents); serving underage customers (10 per cent); infringement of the good repute requirement and violating serving hours rules (both with 6 per cent). We have no information on the various penalties handed down by the individual municipality for non-compliance, but a new question in the 2006 questionnaire asked municipalities to indicate whether they had introduced a penalty point scheme. Under the scheme, for every offence against the Alcohol Act and its regulations a number of points can be issued. The scheme is intended to promote greater awareness within the industry to the consequences of breaking the law. One municipality with a penalty point scheme in use is Haugesund. The number of points depends on the offence. If a licensed establishment or retail business receives more than 8 points within a certain time frame, the licence can be withdrawn for a period of time. In 2007, sixteen municipalities operated a penalty point scheme, a year-on-year rise of ten municipalities. Licenses are rarely withdrawn, and when they are it tends to be for a limited time. Only a small number of municipalities have withdrawn retail licenses according to their own reports, and in 2007 no retail licenses were withdrawn for the entire licensing period, and only thirty-one were withdrawn temporarily in twenty municipalities altogether. Figure 9 Reported reasons for withdrawing retail licenses in 2007 Selling to minors 43 % Obviously under the influence 11 % Opening hours 6 % Other reason 26 % Reprehensible economic conduct The leading reason for withdrawing a retail license is selling alcohol to underage customers (43 per cent). This is followed by «other reasons», which includes for instance allowing a minor to serve the customer alcoholic beverages; failure to file sales accounts with the authorities or to pay sales tax. Fourteen per cent were caused by irregularities with respect to economic repute, 11 per cent by selling to one or more obviously inebriated customer(s), and 6 per cent to offences under the opening hours laws. According to their statements, sixty-three municipalities withdrew a total of 153 serving licenses in %
20 Alcohol Policy A Municipal Responsibility 41 Figure 10 Reported reasons for withdrawing serving licenses in 2007 Opening hours 9 % Other reason 18 % Clearly under the influence 42 % Irregular economic conduct 17 % Underage The reason most serving license are withdrawn is for serving obviously inebriated customers this accounted for 42 per cent of all withdrawals. Next comes «other reasons» with 17 per cent. Examples here include two cases of drug peddling, an unused license, serving outside the delineated area; and failure to file sales accounts with the authorities. Irregularities connected with economic conduct were cited in 20 per cent of the cases, and 14 per cent cited serving underage customers, 9 per cent for violating opening hours laws. Temporary withdrawals were significantly more likely than withdrawals lasting for the remainder of the licensing period. The police may close an establishment which sells or serves alcohol without a license (cf. section 1 8a, Alcohol Act). They may also close for up to two days if necessary in order to prevent disorderly conduct; protect the safety of individuals or the general public; or to prevent or halt violations of the law. Only eleven municipalities reported action by the police to close premises that retailed or served alcoholic beverages in % fail to detect violations that do take place. The evidence, unfortunately, is very strongly in favour of the latter conclusion. Studies by the National Institute for Drug and Alcohol Research show that underage and inebriated customers can both buy and be served alcoholic beverages. A study found that in 50 per cent of cases teenagers could purchase alcohol without being asked to prove their age. This happened in shops and at Vinmonopol outlets. For the purpose of the study, underage-looking eighteen-year-olds tried to buy beer in shops and Vinmonopol outlets. The latter tended to be stricter than the shops, but the differences were small (Rossow, Jarlsson and Raitasalo 2008). Studies of bars and restaurants show that overserving is rife. The studies of businesses in Bergen and Trondheim used actors playing extremely drunk customers to test whether they could get a drink and to see how staff reacted to an obviously drunk customer. In most of these experiments, the «drunk» got what he or she ordered (Holth and Bye 2004; Buvik and Baklien 2006: Lauritzen and Baklien 2007). But for infringements to be detected, inspections must be carried out at the right time, in the right place and by the right people. Reports must be written up and filed and evidence preserved. The model depicted below illustrates the milestones on the long road to license withdrawal (Lauritzen og Baklien 2007). Figure 11 From infringement to withdrawal... Political will to take action The political body commercial and economic votes in favour of weighed against alcohol and public revoking the license health policy goals 5.3 From infringement to withdrawal According to the survey, municipalities are failing to detect unlawful behaviour, and when they do, offences rarely result in penalties. It takes a lot to lose a license in practice, it hardly ever happens. This could indicate a particularly low incidence of unlawful conduct, or that inspectors Council admini - stration assess the the case Inspectors write and file report of observations Inspectors observe overserving to see whether it would stand up in court.inspectors must take the trouble to write the report Vital to be in the right place at the right time and before word reaches the establishment that inspectors are on the way
2A September 23, 2005 SPECIAL SECTION TO IN BUSINESS LAS VEGAS
 2A September 23, 2005 SPECIAL SECTION TO IN BUSINESS LAS VEGAS SPECIAL SECTION TO IN BUSINESS LAS VEGAS 3A September 23, 2005 SEE, PAGE 8A Businesses seek flexibility. It helps them compete in a fast-paced,
2A September 23, 2005 SPECIAL SECTION TO IN BUSINESS LAS VEGAS SPECIAL SECTION TO IN BUSINESS LAS VEGAS 3A September 23, 2005 SEE, PAGE 8A Businesses seek flexibility. It helps them compete in a fast-paced,
Slope-Intercept Formula
 LESSON 7 Slope Intercept Formula LESSON 7 Slope-Intercept Formula Here are two new words that describe lines slope and intercept. The slope is given by m (a mountain has slope and starts with m), and intercept
LESSON 7 Slope Intercept Formula LESSON 7 Slope-Intercept Formula Here are two new words that describe lines slope and intercept. The slope is given by m (a mountain has slope and starts with m), and intercept
Liite 2 A. Sulautuvan Yhtiön nykyinen yhtiöjärjestys
 Liite 2 A Sulautuvan Yhtiön nykyinen yhtiöjärjestys Articles of Association EVRY ASA Updated 11 April 2019 1 Company name The company's name is EVRY ASA. The company is a public limited liability company.
Liite 2 A Sulautuvan Yhtiön nykyinen yhtiöjärjestys Articles of Association EVRY ASA Updated 11 April 2019 1 Company name The company's name is EVRY ASA. The company is a public limited liability company.
Eiendomsverdi. The housing market Update September 2013
 Eiendomsverdi The housing market Update September 2013 Executive summary September is usually a weak month but this was the weakest since 2008. Prices fell by 1.4 percent Volumes were slightly lower than
Eiendomsverdi The housing market Update September 2013 Executive summary September is usually a weak month but this was the weakest since 2008. Prices fell by 1.4 percent Volumes were slightly lower than
PETROLEUMSPRISRÅDET. NORM PRICE FOR ALVHEIM AND NORNE CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL SHELF 1st QUARTER 2016
 1 PETROLEUMSPRISRÅDET Deres ref Vår ref Dato OED 16/716 22.06.2016 To the Licensees (Unofficial translation) NORM PRICE FOR ALVHEIM AND NORNE CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL SHELF 1st QUARTER
1 PETROLEUMSPRISRÅDET Deres ref Vår ref Dato OED 16/716 22.06.2016 To the Licensees (Unofficial translation) NORM PRICE FOR ALVHEIM AND NORNE CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL SHELF 1st QUARTER
EN Skriving for kommunikasjon og tenkning
 EN-435 1 Skriving for kommunikasjon og tenkning Oppgaver Oppgavetype Vurdering 1 EN-435 16/12-15 Introduction Flervalg Automatisk poengsum 2 EN-435 16/12-15 Task 1 Skriveoppgave Manuell poengsum 3 EN-435
EN-435 1 Skriving for kommunikasjon og tenkning Oppgaver Oppgavetype Vurdering 1 EN-435 16/12-15 Introduction Flervalg Automatisk poengsum 2 EN-435 16/12-15 Task 1 Skriveoppgave Manuell poengsum 3 EN-435
STILLAS - STANDARD FORSLAG FRA SEF TIL NY STILLAS - STANDARD
 FORSLAG FRA SEF TIL NY STILLAS - STANDARD 1 Bakgrunnen for dette initiativet fra SEF, er ønsket om å gjøre arbeid i høyden tryggere / sikrere. Både for stillasmontører og brukere av stillaser. 2 Reviderte
FORSLAG FRA SEF TIL NY STILLAS - STANDARD 1 Bakgrunnen for dette initiativet fra SEF, er ønsket om å gjøre arbeid i høyden tryggere / sikrere. Både for stillasmontører og brukere av stillaser. 2 Reviderte
Little Mountain Housing
 Little Mountain Housing Feedback from January 2012 Open Houses Presentation to Little Mountain Community Advisory Group Overview Open house attendance 409 signed in 600+ total Comment forms submitted 326
Little Mountain Housing Feedback from January 2012 Open Houses Presentation to Little Mountain Community Advisory Group Overview Open house attendance 409 signed in 600+ total Comment forms submitted 326
Dagens tema: Eksempel Klisjéer (mønstre) Tommelfingerregler
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO INF1300 Introduksjon til databaser Dagens tema: Eksempel Klisjéer (mønstre) Tommelfingerregler Institutt for informatikk Dumitru Roman 1 Eksempel (1) 1. The system shall give an overview
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO INF1300 Introduksjon til databaser Dagens tema: Eksempel Klisjéer (mønstre) Tommelfingerregler Institutt for informatikk Dumitru Roman 1 Eksempel (1) 1. The system shall give an overview
Unit Relational Algebra 1 1. Relational Algebra 1. Unit 3.3
 Relational Algebra 1 Unit 3.3 Unit 3.3 - Relational Algebra 1 1 Relational Algebra Relational Algebra is : the formal description of how a relational database operates the mathematics which underpin SQL
Relational Algebra 1 Unit 3.3 Unit 3.3 - Relational Algebra 1 1 Relational Algebra Relational Algebra is : the formal description of how a relational database operates the mathematics which underpin SQL
Databases 1. Extended Relational Algebra
 Databases 1 Extended Relational Algebra Relational Algebra What is an Algebra? Mathematical system consisting of: Operands --- variables or values from which new values can be constructed. Operators ---
Databases 1 Extended Relational Algebra Relational Algebra What is an Algebra? Mathematical system consisting of: Operands --- variables or values from which new values can be constructed. Operators ---
Emneevaluering GEOV272 V17
 Emneevaluering GEOV272 V17 Studentenes evaluering av kurset Svarprosent: 36 % (5 av 14 studenter) Hvilket semester er du på? Hva er ditt kjønn? Er du...? Er du...? - Annet PhD Candidate Samsvaret mellom
Emneevaluering GEOV272 V17 Studentenes evaluering av kurset Svarprosent: 36 % (5 av 14 studenter) Hvilket semester er du på? Hva er ditt kjønn? Er du...? Er du...? - Annet PhD Candidate Samsvaret mellom
Endelig ikke-røyker for Kvinner! (Norwegian Edition)
 Endelig ikke-røyker for Kvinner! (Norwegian Edition) Allen Carr Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Endelig ikke-røyker for Kvinner! (Norwegian Edition) Allen Carr Endelig ikke-røyker
Endelig ikke-røyker for Kvinner! (Norwegian Edition) Allen Carr Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Endelig ikke-røyker for Kvinner! (Norwegian Edition) Allen Carr Endelig ikke-røyker
European Crime Prevention Network (EUCPN)
 European Crime Prevention Network (EUCPN) The EUCPN was set up by Council Decision 2001/427/JHA in May 2001 to promote crime prevention activity in EU Member States. Its principal activity is information
European Crime Prevention Network (EUCPN) The EUCPN was set up by Council Decision 2001/427/JHA in May 2001 to promote crime prevention activity in EU Member States. Its principal activity is information
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Eksamen i: ECON1910 Poverty and distribution in developing countries Exam: ECON1910 Poverty and distribution in developing countries Eksamensdag: 1. juni 2011 Sensur
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Eksamen i: ECON1910 Poverty and distribution in developing countries Exam: ECON1910 Poverty and distribution in developing countries Eksamensdag: 1. juni 2011 Sensur
Western Alaska CDQ Program. State of Alaska Department of Community & Economic Development
 Western Alaska State of Alaska Department of Community & Economic Development The CDQ program was formally approved in 1992 by the North Pacific Fishery Management Council and implemented by Governor
Western Alaska State of Alaska Department of Community & Economic Development The CDQ program was formally approved in 1992 by the North Pacific Fishery Management Council and implemented by Governor
6350 Månedstabell / Month table Klasse / Class 1 Tax deduction table (tax to be withheld) 2012
 6350 Månedstabell / Month table Klasse / Class 1 Tax deduction table (tax to be withheld) 2012 100 200 3000 0 0 0 13 38 63 88 113 138 163 4000 188 213 238 263 288 313 338 363 378 386 5000 394 402 410 417
6350 Månedstabell / Month table Klasse / Class 1 Tax deduction table (tax to be withheld) 2012 100 200 3000 0 0 0 13 38 63 88 113 138 163 4000 188 213 238 263 288 313 338 363 378 386 5000 394 402 410 417
Trust in the Personal Data Economy. Nina Chung Mathiesen Digital Consulting
 Trust in the Personal Data Economy Nina Chung Mathiesen Digital Consulting Why does trust matter? 97% of Europeans would be happy for their personal data to be used to inform, make recommendations or add
Trust in the Personal Data Economy Nina Chung Mathiesen Digital Consulting Why does trust matter? 97% of Europeans would be happy for their personal data to be used to inform, make recommendations or add
The regulation requires that everyone at NTNU shall have fire drills and fire prevention courses.
 1 The law The regulation requires that everyone at NTNU shall have fire drills and fire prevention courses. 2. 3 Make your self familiar with: Evacuation routes Manual fire alarms Location of fire extinguishers
1 The law The regulation requires that everyone at NTNU shall have fire drills and fire prevention courses. 2. 3 Make your self familiar with: Evacuation routes Manual fire alarms Location of fire extinguishers
Rusmidler i Norge. Statistikk 03. Alcohol and Drugs in Norway. Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research
 Rusmidler i Norge Statistikk 03 Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Standardtegn i tabellene Standard symbols in the tables Symbol Tall kan ikke forekomme Category not applicable. Data mangler
Rusmidler i Norge Statistikk 03 Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Standardtegn i tabellene Standard symbols in the tables Symbol Tall kan ikke forekomme Category not applicable. Data mangler
Smart High-Side Power Switch BTS730
 PG-DSO20 RoHS compliant (green product) AEC qualified 1 Ω Ω µ Data Sheet 1 V1.0, 2007-12-17 Data Sheet 2 V1.0, 2007-12-17 Ω µ µ Data Sheet 3 V1.0, 2007-12-17 µ µ Data Sheet 4 V1.0, 2007-12-17 Data Sheet
PG-DSO20 RoHS compliant (green product) AEC qualified 1 Ω Ω µ Data Sheet 1 V1.0, 2007-12-17 Data Sheet 2 V1.0, 2007-12-17 Ω µ µ Data Sheet 3 V1.0, 2007-12-17 µ µ Data Sheet 4 V1.0, 2007-12-17 Data Sheet
Building conservation in practice
 Building conservation in practice Aadne Gunnar Sollid Cultural heritage leader in Aust- Agder county. Aust-Agder fylkeskommune 2 Synagogen er blant de eldste eksisterende tresynagogen i Øst-Europa. Den
Building conservation in practice Aadne Gunnar Sollid Cultural heritage leader in Aust- Agder county. Aust-Agder fylkeskommune 2 Synagogen er blant de eldste eksisterende tresynagogen i Øst-Europa. Den
Han Ola of Han Per: A Norwegian-American Comic Strip/En Norsk-amerikansk tegneserie (Skrifter. Serie B, LXIX)
 Han Ola of Han Per: A Norwegian-American Comic Strip/En Norsk-amerikansk tegneserie (Skrifter. Serie B, LXIX) Peter J. Rosendahl Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Han Ola of Han Per:
Han Ola of Han Per: A Norwegian-American Comic Strip/En Norsk-amerikansk tegneserie (Skrifter. Serie B, LXIX) Peter J. Rosendahl Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Han Ola of Han Per:
Accuracy of Alternative Baseline Methods
 Accuracy of Alternative Baseline Methods Dr. Steven Braithwait Christensen Associates Energy Consulting IEPEC - Paris June 2010 Outline Demand response & role of baseline loads Measures of baseline performance
Accuracy of Alternative Baseline Methods Dr. Steven Braithwait Christensen Associates Energy Consulting IEPEC - Paris June 2010 Outline Demand response & role of baseline loads Measures of baseline performance
HONSEL process monitoring
 6 DMSD has stood for process monitoring in fastening technology for more than 25 years. HONSEL re- rivet processing back in 990. DMSD 2G has been continuously improved and optimised since this time. All
6 DMSD has stood for process monitoring in fastening technology for more than 25 years. HONSEL re- rivet processing back in 990. DMSD 2G has been continuously improved and optimised since this time. All
Dynamic Programming Longest Common Subsequence. Class 27
 Dynamic Programming Longest Common Subsequence Class 27 Protein a protein is a complex molecule composed of long single-strand chains of amino acid molecules there are 20 amino acids that make up proteins
Dynamic Programming Longest Common Subsequence Class 27 Protein a protein is a complex molecule composed of long single-strand chains of amino acid molecules there are 20 amino acids that make up proteins
Bostøttesamling
 Bostøttesamling 2016 Teresebjerke@husbankenno 04112016 2 09112016 https://wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=khjy5lwf3tg&feature=youtube 3 09112016 Hva skjer fremover? 4 09112016 «Gode selvbetjeningsløsninger» Kilde:
Bostøttesamling 2016 Teresebjerke@husbankenno 04112016 2 09112016 https://wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=khjy5lwf3tg&feature=youtube 3 09112016 Hva skjer fremover? 4 09112016 «Gode selvbetjeningsløsninger» Kilde:
TEKSTER PH.D.-KANDIDATER FREMDRIFTSRAPPORTERING
 TEKSTER PH.D.-KANDIDATER FREMDRIFTSRAPPORTERING DISTRIBUSJONS-E-POST TIL ALLE KANDIDATER: (Fornavn, etternavn) Den årlige fremdriftsrapporteringen er et viktig tiltak som gjør instituttene og fakultetene
TEKSTER PH.D.-KANDIDATER FREMDRIFTSRAPPORTERING DISTRIBUSJONS-E-POST TIL ALLE KANDIDATER: (Fornavn, etternavn) Den årlige fremdriftsrapporteringen er et viktig tiltak som gjør instituttene og fakultetene
Requirements regarding Safety, Health and the Working Environment (SHWE), and pay and working conditions
 Requirements regarding Safety, Health and the Working Environment (SHWE), and pay and working conditions Vigdis Bjørlo 2016-02-05 Suppliers' obligations in relation to the Construction Client Regulations
Requirements regarding Safety, Health and the Working Environment (SHWE), and pay and working conditions Vigdis Bjørlo 2016-02-05 Suppliers' obligations in relation to the Construction Client Regulations
Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye)
 INF283, HØST 16 Er du? Er du? - Annet Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye) Hvor mye praktisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 =
INF283, HØST 16 Er du? Er du? - Annet Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye) Hvor mye praktisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 =
Passasjerer med psykiske lidelser Hvem kan fly? Grunnprinsipper ved behandling av flyfobi
 Passasjerer med psykiske lidelser Hvem kan fly? Grunnprinsipper ved behandling av flyfobi Øivind Ekeberg 5.september 2008 Akuttmedisinsk avdeling, Ullevål universitetssykehus Avdeling for atferdsfag, Universitetet
Passasjerer med psykiske lidelser Hvem kan fly? Grunnprinsipper ved behandling av flyfobi Øivind Ekeberg 5.september 2008 Akuttmedisinsk avdeling, Ullevål universitetssykehus Avdeling for atferdsfag, Universitetet
(see table on right) 1,500,001 to 3,000, ,001pa to 250,000pa
 UNDERWRITING LIMITS The following tables show our financial and medical underwriting limits effective from 07 July 2017. FINANCIAL LIMITS Protection Financial evidence requirements Additional financial
UNDERWRITING LIMITS The following tables show our financial and medical underwriting limits effective from 07 July 2017. FINANCIAL LIMITS Protection Financial evidence requirements Additional financial
Eksamen ENG1002/1003 Engelsk fellesfag Elevar og privatistar/elever og privatister. Nynorsk/Bokmål
 Eksamen 22.11.2012 ENG1002/1003 Engelsk fellesfag Elevar og privatistar/elever og privatister Nynorsk/Bokmål Nynorsk Eksamensinformasjon Eksamenstid Hjelpemiddel Eksamen varer i 5 timar. Alle hjelpemiddel
Eksamen 22.11.2012 ENG1002/1003 Engelsk fellesfag Elevar og privatistar/elever og privatister Nynorsk/Bokmål Nynorsk Eksamensinformasjon Eksamenstid Hjelpemiddel Eksamen varer i 5 timar. Alle hjelpemiddel
Den som gjør godt, er av Gud (Multilingual Edition)
 Den som gjør godt, er av Gud (Multilingual Edition) Arne Jordly Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Den som gjør godt, er av Gud (Multilingual Edition) Arne Jordly Den som gjør godt,
Den som gjør godt, er av Gud (Multilingual Edition) Arne Jordly Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Den som gjør godt, er av Gud (Multilingual Edition) Arne Jordly Den som gjør godt,
NORM PRICE FOR CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL SHELF 1 st QUARTER 2015
 1 PETROLEUM PRICE BO ARD Our reference Date OED 15/712 15/06/2015 To the Licensees on the Norwegian Continental Shelf (Unofficial translation) NORM PRICE FOR CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL
1 PETROLEUM PRICE BO ARD Our reference Date OED 15/712 15/06/2015 To the Licensees on the Norwegian Continental Shelf (Unofficial translation) NORM PRICE FOR CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL
Exercise 1: Phase Splitter DC Operation
 Exercise 1: DC Operation When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to measure dc operating voltages and currents by using a typical transistor phase splitter circuit. You will verify your
Exercise 1: DC Operation When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to measure dc operating voltages and currents by using a typical transistor phase splitter circuit. You will verify your
2 Valg av møteleder 2 Election of a Chairman of the Meeting
 (OFFICE TRANSLATION) INNKALLING TIL ORDINÆR GENERALFORSAMLING I ISLAND DRILLING COMPANY ASA ORG NR 989 734 229 NOTICE OF ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING OF ISLAND DRILLING COMPANY ASA REG NO 989 734 229 Den 9 juni
(OFFICE TRANSLATION) INNKALLING TIL ORDINÆR GENERALFORSAMLING I ISLAND DRILLING COMPANY ASA ORG NR 989 734 229 NOTICE OF ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING OF ISLAND DRILLING COMPANY ASA REG NO 989 734 229 Den 9 juni
Trigonometric Substitution
 Trigonometric Substitution Alvin Lin Calculus II: August 06 - December 06 Trigonometric Substitution sin 4 (x) cos (x) dx When you have a product of sin and cos of different powers, you have three different
Trigonometric Substitution Alvin Lin Calculus II: August 06 - December 06 Trigonometric Substitution sin 4 (x) cos (x) dx When you have a product of sin and cos of different powers, you have three different
ADDENDUM SHAREHOLDERS AGREEMENT. by and between. Aker ASA ( Aker ) and. Investor Investments Holding AB ( Investor ) and. SAAB AB (publ.
 ADDENDUM SHAREHOLDERS AGREEMENT by between Aker ASA ( Aker ) Investor Investments Holding AB ( Investor ) SAAB AB (publ.) ( SAAB ) The Kingdom of Norway acting by the Ministry of Trade Industry ( Ministry
ADDENDUM SHAREHOLDERS AGREEMENT by between Aker ASA ( Aker ) Investor Investments Holding AB ( Investor ) SAAB AB (publ.) ( SAAB ) The Kingdom of Norway acting by the Ministry of Trade Industry ( Ministry
TEKSTER PH.D.-VEILEDERE FREMDRIFTSRAPPORTERING DISTRIBUSJONS-E-POST TIL ALLE AKTUELLE VEILEDERE:
 TEKSTER PH.D.-VEILEDERE FREMDRIFTSRAPPORTERING DISTRIBUSJONS-E-POST TIL ALLE AKTUELLE VEILEDERE: Kjære , hovedveileder for Den årlige fremdriftsrapporteringen er et viktig tiltak som gjør
TEKSTER PH.D.-VEILEDERE FREMDRIFTSRAPPORTERING DISTRIBUSJONS-E-POST TIL ALLE AKTUELLE VEILEDERE: Kjære , hovedveileder for Den årlige fremdriftsrapporteringen er et viktig tiltak som gjør
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS
 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Postponed exam: ECON420 Mathematics 2: Calculus and linear algebra Date of exam: Tuesday, June 8, 203 Time for exam: 09:00 a.m. 2:00 noon The problem set covers
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Postponed exam: ECON420 Mathematics 2: Calculus and linear algebra Date of exam: Tuesday, June 8, 203 Time for exam: 09:00 a.m. 2:00 noon The problem set covers
Nærings-PhD i Aker Solutions
 part of Aker Motivasjon og erfaringer Kristin M. Berntsen/Soffi Westin/Maung K. Sein 09.12.2011 2011 Aker Solutions Motivasjon for Aker Solutions Forutsetning Vilje fra bedrift og se nytteverdien av forskning.
part of Aker Motivasjon og erfaringer Kristin M. Berntsen/Soffi Westin/Maung K. Sein 09.12.2011 2011 Aker Solutions Motivasjon for Aker Solutions Forutsetning Vilje fra bedrift og se nytteverdien av forskning.
Administrasjon av postnummersystemet i Norge Post code administration in Norway. Frode Wold, Norway Post Nordic Address Forum, Iceland 5-6.
 Administrasjon av postnummersystemet i Norge Frode Wold, Norway Post Nordic Address Forum, Iceland 5-6. may 2015 Postnumrene i Norge ble opprettet 18.3.1968 The postal codes in Norway was established in
Administrasjon av postnummersystemet i Norge Frode Wold, Norway Post Nordic Address Forum, Iceland 5-6. may 2015 Postnumrene i Norge ble opprettet 18.3.1968 The postal codes in Norway was established in
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT BOKMÅL Eksamen i: ECON1210 - Forbruker, bedrift og marked Eksamensdag: 26.11.2013 Sensur kunngjøres: 18.12.2013 Tid for eksamen: kl. 14:30-17:30 Oppgavesettet er
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT BOKMÅL Eksamen i: ECON1210 - Forbruker, bedrift og marked Eksamensdag: 26.11.2013 Sensur kunngjøres: 18.12.2013 Tid for eksamen: kl. 14:30-17:30 Oppgavesettet er
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Utsatt eksamen i: ECON1410 - Internasjonal økonomi Exam: ECON1410 - International economics Eksamensdag: 18.06.2013 Date of exam: 18.06.2013 Tid for eksamen: kl.
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Utsatt eksamen i: ECON1410 - Internasjonal økonomi Exam: ECON1410 - International economics Eksamensdag: 18.06.2013 Date of exam: 18.06.2013 Tid for eksamen: kl.
C13 Kokstad. Svar på spørsmål til kvalifikasjonsfasen. Answers to question in the pre-qualification phase For English: See page 4 and forward
 C13 Kokstad Svar på spørsmål til kvalifikasjonsfasen Answers to question in the pre-qualification phase For English: See page 4 and forward Norsk Innhold 1. Innledning... 2 2. Spørsmål mottatt per 28.11.12...
C13 Kokstad Svar på spørsmål til kvalifikasjonsfasen Answers to question in the pre-qualification phase For English: See page 4 and forward Norsk Innhold 1. Innledning... 2 2. Spørsmål mottatt per 28.11.12...
0100 Månedstabell/Month table Trekktabell 2010
 0100 Månedstabell/Month table Trekktabell 2010 Klasse / Class 1 For skatt av sjømannsinntekt med 10% standardfradrag, 30% sjømannsfradrag Trekk- 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 gr.lag 100 200 Tabellen
0100 Månedstabell/Month table Trekktabell 2010 Klasse / Class 1 For skatt av sjømannsinntekt med 10% standardfradrag, 30% sjømannsfradrag Trekk- 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 gr.lag 100 200 Tabellen
Prosjektet Digital kontaktinformasjon og fullmakter for virksomheter Digital contact information and mandates for entities
 Prosjektet Digital kontaktinformasjon og fullmakter for virksomheter Digital contact information and mandates for entities Nordisk Adressemøte / Nordic Address Forum, Stockholm 9-10 May 2017 Elin Strandheim,
Prosjektet Digital kontaktinformasjon og fullmakter for virksomheter Digital contact information and mandates for entities Nordisk Adressemøte / Nordic Address Forum, Stockholm 9-10 May 2017 Elin Strandheim,
Familieeide selskaper - Kjennetegn - Styrker og utfordringer - Vekst og nyskapning i harmoni med tradisjoner
 Familieeide selskaper - Kjennetegn - Styrker og utfordringer - Vekst og nyskapning i harmoni med tradisjoner Resultater fra omfattende internasjonal undersøkelse og betraktninger om hvordan observasjonene
Familieeide selskaper - Kjennetegn - Styrker og utfordringer - Vekst og nyskapning i harmoni med tradisjoner Resultater fra omfattende internasjonal undersøkelse og betraktninger om hvordan observasjonene
Hvor mye praktisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye)
 INF247 Er du? Er du? - Annet Ph.D. Student Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye) Hvor mye praktisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen,
INF247 Er du? Er du? - Annet Ph.D. Student Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye) Hvor mye praktisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen,
KROPPEN LEDER STRØM. Sett en finger på hvert av kontaktpunktene på modellen. Da får du et lydsignal.
 KROPPEN LEDER STRØM Sett en finger på hvert av kontaktpunktene på modellen. Da får du et lydsignal. Hva forteller dette signalet? Gå flere sammen. Ta hverandre i hendene, og la de to ytterste personene
KROPPEN LEDER STRØM Sett en finger på hvert av kontaktpunktene på modellen. Da får du et lydsignal. Hva forteller dette signalet? Gå flere sammen. Ta hverandre i hendene, og la de to ytterste personene
5 E Lesson: Solving Monohybrid Punnett Squares with Coding
 5 E Lesson: Solving Monohybrid Punnett Squares with Coding Genetics Fill in the Brown colour Blank Options Hair texture A field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to
5 E Lesson: Solving Monohybrid Punnett Squares with Coding Genetics Fill in the Brown colour Blank Options Hair texture A field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to
Baltic Sea Region CCS Forum. Nordic energy cooperation perspectives
 Norsk mal: Startside Baltic Sea Region CCS Forum. Nordic energy cooperation perspectives Johan Vetlesen. Senior Energy Committe of the Nordic Council of Ministers 22-23. april 2015 Nordic Council of Ministers.
Norsk mal: Startside Baltic Sea Region CCS Forum. Nordic energy cooperation perspectives Johan Vetlesen. Senior Energy Committe of the Nordic Council of Ministers 22-23. april 2015 Nordic Council of Ministers.
Issues and challenges in compilation of activity accounts
 1 Issues and challenges in compilation of activity accounts London Group on environmental accounting 21st meeting 2-4 November 2015 Statistics Netherlands The Hague Kristine E. Kolshus kre@ssb.no Statistics
1 Issues and challenges in compilation of activity accounts London Group on environmental accounting 21st meeting 2-4 November 2015 Statistics Netherlands The Hague Kristine E. Kolshus kre@ssb.no Statistics
Stipend fra Jubileumsfondet skoleåret 2002-2003
 Til skolen Rundskriv S 09-2002 Oslo, 15. februar 2002 Stipend fra Jubileumsfondet skoleåret 2002-2003 For nærmere omtale av H.M. Kong Olav V s Jubileumsfond viser vi til NKF-handboka kap. 12.3.4. Fondet
Til skolen Rundskriv S 09-2002 Oslo, 15. februar 2002 Stipend fra Jubileumsfondet skoleåret 2002-2003 For nærmere omtale av H.M. Kong Olav V s Jubileumsfond viser vi til NKF-handboka kap. 12.3.4. Fondet
Kartleggingsskjema / Survey
 Kartleggingsskjema / Survey 1. Informasjon om opphold i Norge / Information on resident permit in Norway Hvilken oppholdstillatelse har du i Norge? / What residence permit do you have in Norway? YES No
Kartleggingsskjema / Survey 1. Informasjon om opphold i Norge / Information on resident permit in Norway Hvilken oppholdstillatelse har du i Norge? / What residence permit do you have in Norway? YES No
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Eksamen i: ECON360/460 Samfunnsøkonomisk lønnsomhet og økonomisk politikk Exam: ECON360/460 - Resource allocation and economic policy Eksamensdag: Fredag 2. november
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Eksamen i: ECON360/460 Samfunnsøkonomisk lønnsomhet og økonomisk politikk Exam: ECON360/460 - Resource allocation and economic policy Eksamensdag: Fredag 2. november
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Eksamen i: ECON1310 Økonomisk aktivitet og økonomisk politikk Exam: ECON1310 Macroeconomic theory and policy Eksamensdag: 18.05.01 Sensur blir annonsert: 07.06.01
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Eksamen i: ECON1310 Økonomisk aktivitet og økonomisk politikk Exam: ECON1310 Macroeconomic theory and policy Eksamensdag: 18.05.01 Sensur blir annonsert: 07.06.01
Hungary, 1st quarter 2019
 Hungary, 1st quarter Macroeconomy The GDP of the European Union, our immediate economic environment according to seasonally and working-day-adjusted data grew by 1.5% compared to the same period of the
Hungary, 1st quarter Macroeconomy The GDP of the European Union, our immediate economic environment according to seasonally and working-day-adjusted data grew by 1.5% compared to the same period of the
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Bokmål Eksamen i: ECON1210 Forbruker, bedrift og marked Exam: ECON1210 Consumer Behaviour, Firm behaviour and Markets Eksamensdag: 12.12.2014 Sensur kunngjøres:
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Bokmål Eksamen i: ECON1210 Forbruker, bedrift og marked Exam: ECON1210 Consumer Behaviour, Firm behaviour and Markets Eksamensdag: 12.12.2014 Sensur kunngjøres:
SUPPLIER UPDATE. September 23, 2015
 1 SUPPLIER UPDATE September 23, 2015 Agenda 2 Clarify and document Supplier Collateral Requirement New Customer Information Agreement Review Customer Education campaign Q&A Credit Requirements For Suppliers
1 SUPPLIER UPDATE September 23, 2015 Agenda 2 Clarify and document Supplier Collateral Requirement New Customer Information Agreement Review Customer Education campaign Q&A Credit Requirements For Suppliers
Du kan bruke det vedlagte skjemaet Egenerklæring skattemessig bosted 2012 når du søker om frikort.
 Skatteetaten Saksbehandler Deres dato Vår dato 28.10.2011 Telefon Deres Vår referanse For information in English see page 3 Skattekort for 2012 Du fikk helt eller delvis skattefritak ved likningen for
Skatteetaten Saksbehandler Deres dato Vår dato 28.10.2011 Telefon Deres Vår referanse For information in English see page 3 Skattekort for 2012 Du fikk helt eller delvis skattefritak ved likningen for
 Vedlegg 1 / appendix 1 FORTEGNELSE OVER MØTENDE AKSJEEIERE, ORDINÆR GENERALFORSAMLING GLOBAL RIG COMPANY, 26 MAI 2009 Navn Aksjer/stemmer Representert ved SECTOR UMBRELLA TRUST-SECTOR SPECULARE PR EQ IV
Vedlegg 1 / appendix 1 FORTEGNELSE OVER MØTENDE AKSJEEIERE, ORDINÆR GENERALFORSAMLING GLOBAL RIG COMPANY, 26 MAI 2009 Navn Aksjer/stemmer Representert ved SECTOR UMBRELLA TRUST-SECTOR SPECULARE PR EQ IV
INSTRUKS FOR VALGKOMITEEN I AKASTOR ASA (Fastsatt på generalforsamling i Akastor ASA (tidligere Aker Solutions ASA) 6. mai 2011)
 INSTRUKS FOR VALGKOMITEEN I AKASTOR ASA (Fastsatt på generalforsamling i Akastor ASA (tidligere Aker Solutions ASA) 6. mai 2011) 1 Oppgaver Valgkomiteens oppgaver er å avgi innstilling til - generalforsamlingen
INSTRUKS FOR VALGKOMITEEN I AKASTOR ASA (Fastsatt på generalforsamling i Akastor ASA (tidligere Aker Solutions ASA) 6. mai 2011) 1 Oppgaver Valgkomiteens oppgaver er å avgi innstilling til - generalforsamlingen
0100 Månedstabell/Month table Trekktabell 2013
 0100 Månedstabell/Month table Trekktabell 2013 Klasse / Class 1 For skatt av sjømannsinntekt med 10% standardfradrag, 30% sjømannsfradrag Trekk- 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0100 Månedstabell/Month table Trekktabell 2013 Klasse / Class 1 For skatt av sjømannsinntekt med 10% standardfradrag, 30% sjømannsfradrag Trekk- 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2018 ANNUAL SPONSORSHIP OPPORTUNITIES
 ANNUAL SPONSORSHIP OPPORTUNITIES MVP SPONSORSHIP PROGRAM CALLING ALL VENDORS! Here is your chance to gain company exposure while strengthening your dealer Association at the same time. Annual Sponsorship
ANNUAL SPONSORSHIP OPPORTUNITIES MVP SPONSORSHIP PROGRAM CALLING ALL VENDORS! Here is your chance to gain company exposure while strengthening your dealer Association at the same time. Annual Sponsorship
Avgjørelse patent - Meddelelse av søknad
 Curo AS Industriveien 53 7080 HEIMDAL Oslo, 2016.02.10 Deres ref.: U3206 Søknadsnr.: 20140317 Avgjørelse patent - Meddelelse av søknad 20140317 Vi har nå meddelt ditt patent. Patentbrev er vedlagt 1. Frist
Curo AS Industriveien 53 7080 HEIMDAL Oslo, 2016.02.10 Deres ref.: U3206 Søknadsnr.: 20140317 Avgjørelse patent - Meddelelse av søknad 20140317 Vi har nå meddelt ditt patent. Patentbrev er vedlagt 1. Frist
Rusmidler i Norge. Statistikk 07. Alcohol and Drugs in Norway. Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research
 Rusmidler i Norge Statistikk 7 Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Standardtegn i tabellene Standard symbols in the tables Symbol Tall kan ikke forekomme Category not applicable. Data mangler
Rusmidler i Norge Statistikk 7 Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Standardtegn i tabellene Standard symbols in the tables Symbol Tall kan ikke forekomme Category not applicable. Data mangler
Nåværende EU-rett Dir 96/3/EC
 Article 1 Derogation By way of derogation to point 4 of Chapter IV of Annex II to Regulation EC (No) 852/2004, liquid oils or fats which are intended for or likely to be used for human consumption ('oils
Article 1 Derogation By way of derogation to point 4 of Chapter IV of Annex II to Regulation EC (No) 852/2004, liquid oils or fats which are intended for or likely to be used for human consumption ('oils
PETROLEUMSPRISRÅDET. Deres ref Vår ref Dato OED 18/
 1 PETROLEUMSPRISRÅDET Deres ref Vår ref Dato OED 18/763 19.10.2018 To the licensees on the Norwegian Continental Shelf (Unofficial translation) NORM PRICE FOR CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL
1 PETROLEUMSPRISRÅDET Deres ref Vår ref Dato OED 18/763 19.10.2018 To the licensees on the Norwegian Continental Shelf (Unofficial translation) NORM PRICE FOR CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL
Vedlegg 4 Forslag til reviderte vedtekter
 Vedlegg 4 Forslag til reviderte vedtekter In case of discrepancy between the Norwegian and the English text, the Norwegian text shall prevail 1 Navn Selskapets navn er Fjordkraft Holding ASA. 2 Selskapsform
Vedlegg 4 Forslag til reviderte vedtekter In case of discrepancy between the Norwegian and the English text, the Norwegian text shall prevail 1 Navn Selskapets navn er Fjordkraft Holding ASA. 2 Selskapsform
(see table on right) 1,500,001 to 3,000, ,001pa to 250,000pa
 UNDERWRITING LIMITS The following tables show our financial and medical underwriting limits effective from 11 April 2016. FINANCIAL LIMITS Protection Financial evidence requirements Additional financial
UNDERWRITING LIMITS The following tables show our financial and medical underwriting limits effective from 11 April 2016. FINANCIAL LIMITS Protection Financial evidence requirements Additional financial
Software applications developed for the maritime service at the Danish Meteorological Institute
 Software applications developed for the maritime service at the Danish Meteorological Institute Anne Marie Munk Jørgensen (ammj@dmi.dk), Ove Kjær, Knud E. Christensen & Morten L. Mortensen Danish Meteorological
Software applications developed for the maritime service at the Danish Meteorological Institute Anne Marie Munk Jørgensen (ammj@dmi.dk), Ove Kjær, Knud E. Christensen & Morten L. Mortensen Danish Meteorological
Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye)
 INF234 Er du? Er du? - Annet Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye) Hvor mye praktisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye) Hvor
INF234 Er du? Er du? - Annet Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye) Hvor mye praktisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye) Hvor
0:7 0:2 0:1 0:3 0:5 0:2 0:1 0:4 0:5 P = 0:56 0:28 0:16 0:38 0:39 0:23
 UTKAST ENGLISH VERSION EKSAMEN I: MOT100A STOKASTISKE PROSESSER VARIGHET: 4 TIMER DATO: 16. februar 2006 TILLATTE HJELPEMIDLER: Kalkulator; Tabeller og formler i statistikk (Tapir forlag): Rottman: Matematisk
UTKAST ENGLISH VERSION EKSAMEN I: MOT100A STOKASTISKE PROSESSER VARIGHET: 4 TIMER DATO: 16. februar 2006 TILLATTE HJELPEMIDLER: Kalkulator; Tabeller og formler i statistikk (Tapir forlag): Rottman: Matematisk
ATO program for Renewal of IR, Class or Type-rating
 May be used by the ATO in order to establish an individual training program for renewal of IR, Class or Type-rating in accordance with FCL.625 IR(c)(d) / AMC1 FCL.625(c) and FCL.740(b)(1)(2) / AMC1 FCL.740(b)(1)
May be used by the ATO in order to establish an individual training program for renewal of IR, Class or Type-rating in accordance with FCL.625 IR(c)(d) / AMC1 FCL.625(c) and FCL.740(b)(1)(2) / AMC1 FCL.740(b)(1)
Den europeiske byggenæringen blir digital. hva skjer i Europa? Steen Sunesen Oslo,
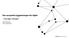 Den europeiske byggenæringen blir digital hva skjer i Europa? Steen Sunesen Oslo, 30.04.2019 Agenda 1. 2. CEN-veileder til ISO 19650 del 1 og 2 3. EFCA Guide Oppdragsgivers krav til BIMleveranser og prosess.
Den europeiske byggenæringen blir digital hva skjer i Europa? Steen Sunesen Oslo, 30.04.2019 Agenda 1. 2. CEN-veileder til ISO 19650 del 1 og 2 3. EFCA Guide Oppdragsgivers krav til BIMleveranser og prosess.
Gol Statlige Mottak. Modul 7. Ekteskapsloven
 Gol Statlige Mottak Modul 7 Ekteskapsloven Paragraphs in Norwegian marriage law 1.Kjønn To personer av motsatt eller samme kjønn kan inngå ekteskap. Two persons of opposite or same sex can marry 1 a. Ekteskapsalder.
Gol Statlige Mottak Modul 7 Ekteskapsloven Paragraphs in Norwegian marriage law 1.Kjønn To personer av motsatt eller samme kjønn kan inngå ekteskap. Two persons of opposite or same sex can marry 1 a. Ekteskapsalder.
Forecast Methodology September LightCounting Market Research Notes
 Forecast Methodology September 2015 LightCounting Market Research Notes Vladimir Market Kozlov Forecast Methodology, September, September, 2015 2015 1 Summary In summary, the key assump=on of our forecast
Forecast Methodology September 2015 LightCounting Market Research Notes Vladimir Market Kozlov Forecast Methodology, September, September, 2015 2015 1 Summary In summary, the key assump=on of our forecast
CAMES. Technical. Skills. Overskrift 27pt i to eller flere linjer teksten vokser opad. Brødtekst 22pt skrives her. Andet niveau.
 CAMES Overskrift 27pt i to eller flere linjer Technical Skills Leizl Joy Nayahangan, RN, MHCM Leizl.joy.nayahangan@regionh.dk IMPORTANCE Challenges Brødtekst 22pt of patient skrives her care Increasing
CAMES Overskrift 27pt i to eller flere linjer Technical Skills Leizl Joy Nayahangan, RN, MHCM Leizl.joy.nayahangan@regionh.dk IMPORTANCE Challenges Brødtekst 22pt of patient skrives her care Increasing
(Notification of attendance Proxy documents: English version follows below)
 MØTESEDDEL OG FULLMAKTSSKJEMA (Notification of attendance Proxy documents: English version follows below) i forbindelse med ekstraordinær generalforsamling i som avholdes 24.11.2017 kl. 09:30 i Lilleakerveien
MØTESEDDEL OG FULLMAKTSSKJEMA (Notification of attendance Proxy documents: English version follows below) i forbindelse med ekstraordinær generalforsamling i som avholdes 24.11.2017 kl. 09:30 i Lilleakerveien
Independent Inspection
 Independent Inspection Odd Ivar Johnsen Vidar Nystad Independent Inspection Mål: Felles forståelse og utøvelse av "Independent Inspection" i forbindelse med "Critical Maintenance Task". Independent Inspection
Independent Inspection Odd Ivar Johnsen Vidar Nystad Independent Inspection Mål: Felles forståelse og utøvelse av "Independent Inspection" i forbindelse med "Critical Maintenance Task". Independent Inspection
GEO231 Teorier om migrasjon og utvikling
 U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Institutt for geografi Emnerapport høsten 2013: GEO231 Teorier om migrasjon og utvikling Innhold: 1. Informasjon om emnet 2. Statistikk 3. Egenevaluering 4. Studentevaluering
U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Institutt for geografi Emnerapport høsten 2013: GEO231 Teorier om migrasjon og utvikling Innhold: 1. Informasjon om emnet 2. Statistikk 3. Egenevaluering 4. Studentevaluering
Neural Network. Sensors Sorter
 CSC 302 1.5 Neural Networks Simple Neural Nets for Pattern Recognition 1 Apple-Banana Sorter Neural Network Sensors Sorter Apples Bananas 2 Prototype Vectors Measurement vector p = [shape, texture, weight]
CSC 302 1.5 Neural Networks Simple Neural Nets for Pattern Recognition 1 Apple-Banana Sorter Neural Network Sensors Sorter Apples Bananas 2 Prototype Vectors Measurement vector p = [shape, texture, weight]
PETROLEUM PRICE BOARD
 1 PETROLEUM PRICE BOARD Our reference Date OED 15/712 21/09/2015 To the Licensees on the Norwegian Continental Shelf (Unofficial translation) NORM PRICE FOR CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL
1 PETROLEUM PRICE BOARD Our reference Date OED 15/712 21/09/2015 To the Licensees on the Norwegian Continental Shelf (Unofficial translation) NORM PRICE FOR CRUDE OIL PRODUCED ON THE NORWEGIAN CONTINENTAL
Hvor mye teoretisk kunnskap har du tilegnet deg på dette emnet? (1 = ingen, 5 = mye)
 Emneevaluering GEOV325 Vår 2016 Kommentarer til GEOV325 VÅR 2016 (emneansvarlig) Forelesingsrommet inneholdt ikke gode nok muligheter for å kunne skrive på tavle og samtidig ha mulighet for bruk av power
Emneevaluering GEOV325 Vår 2016 Kommentarer til GEOV325 VÅR 2016 (emneansvarlig) Forelesingsrommet inneholdt ikke gode nok muligheter for å kunne skrive på tavle og samtidig ha mulighet for bruk av power
Monitoring water sources.
 Monitoring water sources. Generell Informasjon Versjon 2 Url http://com.mercell.com/permalink/38336681.aspx Ekstern anbuds ID 223314-2013 Konkurranse type: Tildeling Dokument type Kontraktstildeling Prosedyre
Monitoring water sources. Generell Informasjon Versjon 2 Url http://com.mercell.com/permalink/38336681.aspx Ekstern anbuds ID 223314-2013 Konkurranse type: Tildeling Dokument type Kontraktstildeling Prosedyre
Assessing second language skills - a challenge for teachers Case studies from three Norwegian primary schools
 Assessing second language skills - a challenge for teachers Case studies from three Norwegian primary schools The Visions Conference 2011 UiO 18 20 May 2011 Kirsten Palm Oslo University College Else Ryen
Assessing second language skills - a challenge for teachers Case studies from three Norwegian primary schools The Visions Conference 2011 UiO 18 20 May 2011 Kirsten Palm Oslo University College Else Ryen
PHIL 102, Fall 2013 Christina Hendricks
 PHIL 102, Fall 2013 Christina Hendricks Peter Singer Australian, now at Princeton University Clip from a documentary called Examined Life, giving an overview of Singer s views on poverty and ethical treatment
PHIL 102, Fall 2013 Christina Hendricks Peter Singer Australian, now at Princeton University Clip from a documentary called Examined Life, giving an overview of Singer s views on poverty and ethical treatment
Nytt EU-direktiv om forebygging av stikkskader, betydning for oss? Dorthea Hagen Oma Smittevernlege Helse Bergen
 Nytt EU-direktiv om forebygging av stikkskader, betydning for oss? Dorthea Hagen Oma Smittevernlege Helse Bergen The EU Sharps Directive blei vedtatt i mai 2010 direktivet er juridisk bindande også i
Nytt EU-direktiv om forebygging av stikkskader, betydning for oss? Dorthea Hagen Oma Smittevernlege Helse Bergen The EU Sharps Directive blei vedtatt i mai 2010 direktivet er juridisk bindande også i
2 Valg av møteleder 2 Election of a Chairman of the Meeting
 (OFFICE TRANSLATION) INNKALLING TIL ORDINÆR GENERALFORSAMLING I MARACC- MARINE ACCURATE WELL ASA ORG NR 989 734 229 NOTICE OF ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING OF MARACC- MARINE ACCURATE WELL ASA REG NO 989 734 229
(OFFICE TRANSLATION) INNKALLING TIL ORDINÆR GENERALFORSAMLING I MARACC- MARINE ACCURATE WELL ASA ORG NR 989 734 229 NOTICE OF ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING OF MARACC- MARINE ACCURATE WELL ASA REG NO 989 734 229
Rusmidler i Norge. Statistikk 05. Alcohol and Drugs in Norway. Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research
 Rusmidler i Norge Statistikk 05 Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Standardtegn i tabellene Standard symbols in the tables Symbol Tall kan ikke forekomme Category not applicable. Data mangler
Rusmidler i Norge Statistikk 05 Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Standardtegn i tabellene Standard symbols in the tables Symbol Tall kan ikke forekomme Category not applicable. Data mangler
Endringer i neste revisjon av EHF / Changes in the next revision of EHF 1. October 2015
 Endringer i neste revisjon av / Changes in the next revision of 1. October 2015 INFORMASJON PÅ NORSK 2 INTRODUKSJON 2 ENDRINGER FOR KATALOG 1.0.3 OG PAKKSEDDEL 1.0.2 3 ENDRINGER FOR ORDRE 1.0.3 4 ENDRINGER
Endringer i neste revisjon av / Changes in the next revision of 1. October 2015 INFORMASJON PÅ NORSK 2 INTRODUKSJON 2 ENDRINGER FOR KATALOG 1.0.3 OG PAKKSEDDEL 1.0.2 3 ENDRINGER FOR ORDRE 1.0.3 4 ENDRINGER
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Eksamen i: ECON20 Forbruker, bedrift og marked, høsten 2004 Exam: ECON20 - Consumer behavior, firm behavior and markets, autumn 2004 Eksamensdag: Onsdag 24. november
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO ØKONOMISK INSTITUTT Eksamen i: ECON20 Forbruker, bedrift og marked, høsten 2004 Exam: ECON20 - Consumer behavior, firm behavior and markets, autumn 2004 Eksamensdag: Onsdag 24. november
Hvordan ser pasientene oss?
 Hvordan ser pasientene oss? Safio Bilqeyr Jimale og Arild Aambø Migrasjonshelse PMU 2018 Hva gruer du mest for når du skal til legen? Konsultasjonstiden strekker ikke til Legene ser bare det som er interessant
Hvordan ser pasientene oss? Safio Bilqeyr Jimale og Arild Aambø Migrasjonshelse PMU 2018 Hva gruer du mest for når du skal til legen? Konsultasjonstiden strekker ikke til Legene ser bare det som er interessant
Nøtteknekkeren fem år etter
 part of Aker Geir Arne Drangeid Konserndirektør kommunikasjon 13. april 2011 2011 Aker Solutions Film skal legges inn her Slide 2 Formidlingskraft Aker er en viktig hjørnestensbedrift i det norske samfunnet
part of Aker Geir Arne Drangeid Konserndirektør kommunikasjon 13. april 2011 2011 Aker Solutions Film skal legges inn her Slide 2 Formidlingskraft Aker er en viktig hjørnestensbedrift i det norske samfunnet
Invitation to Tender FSP FLO-IKT /2013/001 MILS OS
 Invitation to Tender FSP FLO-IKT /2013/001 MILS OS April 15th 2013 Forfatter Prosjektittel 19.04.2013 19.04.2013 1 Introduction AGENDA Important aspects regarding the competition and Invitation to tender
Invitation to Tender FSP FLO-IKT /2013/001 MILS OS April 15th 2013 Forfatter Prosjektittel 19.04.2013 19.04.2013 1 Introduction AGENDA Important aspects regarding the competition and Invitation to tender
Haakon VII s gt. 1, Oslo mandag 23. januar 2006 kl 10:00.
 Til aksjeeierne i Songa ASA INNKALLING TIL EKSTRAORDINÆR GENERALFORSAMLING Ekstraordinær generalforsamling i Songa ASA holdes på selskapets kontor i Haakon VII s gt. 1, Oslo mandag 23. januar 2006 kl 10:00.
Til aksjeeierne i Songa ASA INNKALLING TIL EKSTRAORDINÆR GENERALFORSAMLING Ekstraordinær generalforsamling i Songa ASA holdes på selskapets kontor i Haakon VII s gt. 1, Oslo mandag 23. januar 2006 kl 10:00.
Materials relating to 2013 North Dakota legislative action concerning setbacks for oil and gas wells
 Materials relating to 2013 North Dakota legislative action concerning setbacks for oil and gas wells N.D.C.C. 38-08-01, 2012 and 2018 version: 38-08-01. Declaration of policy. It is hereby declared to
Materials relating to 2013 North Dakota legislative action concerning setbacks for oil and gas wells N.D.C.C. 38-08-01, 2012 and 2018 version: 38-08-01. Declaration of policy. It is hereby declared to
Rusmidler i Norge. Statistikk 06. Alcohol and Drugs in Norway. Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research
 Rusmidler i Norge Statistikk 06 Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Standardtegn i tabellene Standard symbols in the tables Symbol Tall kan ikke forekomme Category not applicable. Data mangler
Rusmidler i Norge Statistikk 06 Norwegian Institute for Alcohol and Drug Research Standardtegn i tabellene Standard symbols in the tables Symbol Tall kan ikke forekomme Category not applicable. Data mangler
